PRODUCTS DETAILS
Copper Clad Aluminum Busbar
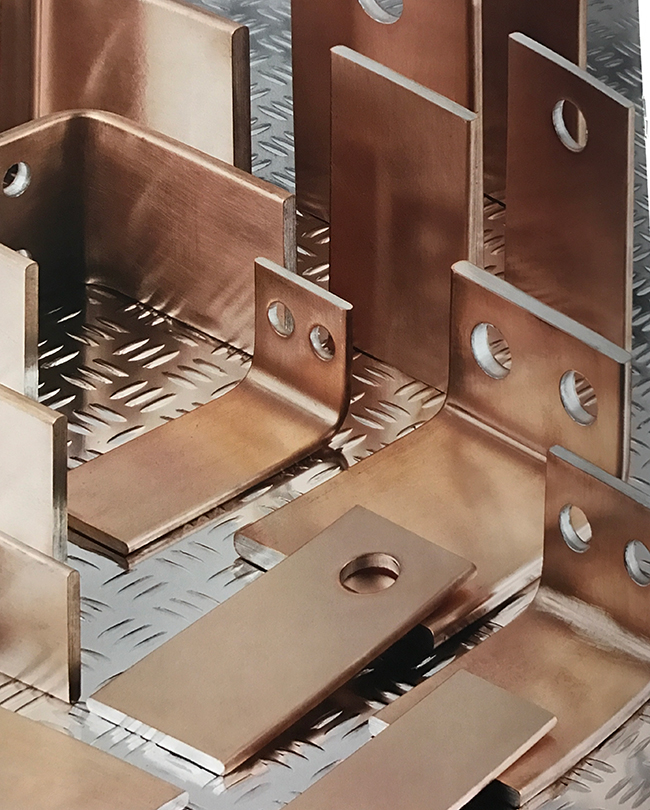
What is the busbar?
Busbar, a metallic strip or bar, typically housed inside switchgear, panel boards, and busway enclosures for local high current power distribution. They are also used to connect high voltage equipment at electrical switchyards, and low voltage equipment in battery banks. They are generally uninsulated, and have sufficient stiffness to be supported in air by insulated pillars. These features allow sufficient cooling of the conductors, and the ability to tap in at various points without creating a new joint.
The material composition and cross-sectional size of the busbar determine the maximum amount of current that can be safely carried. Busbars are produced in a variety of shapes, such as flat strips, solid bars, or rods, and are typically composed of copper, brass, or aluminium. The skin effect makes 50~60Hz AC busbars more than about 8 millimeters (0.31 in) thickness inefficient, so flat shapes are prevalent in higher current applications.
Bus bars reduce system costs, improve reliability, increase capacitance, and eliminate wiring errors. They also lower inductance and increase capacitance. Plus, the physical structure of bus bars offers unique features in mechanical design.
What is Copper Clad Aluminum Busbar (CCA Busbar)?
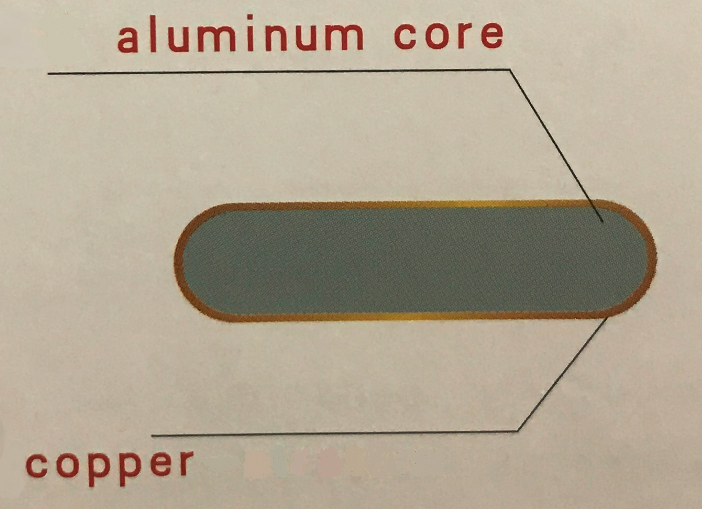
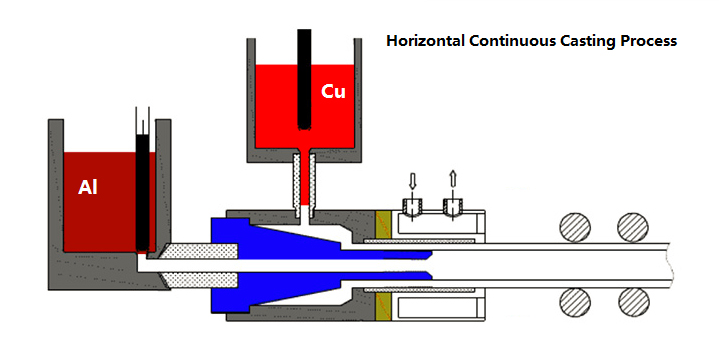
It is a new bimetallic material, using Horizontal Continuous Casting Process, not copper cladding technology. From copper by volume, it can be divided 25% and 30%.
Copper by Volume | State | Density (g/cm³) | Tensile Strength (Mpa) | Elongation | D.C. at 20℃ (Ω·mm²/m) |
25% | Hard | 4.25 | ≥170 | ≥2% | ≤0.02548 |
Soft | 4.25 | ≥115 | ≥25% | ≤0.02498 | |
30% | Hard | 4.56 | ≥180 | ≥2% | ≤0.02477 |
Soft | 4.56 | ≥120 | ≥28% | ≤0.02424 |
Current Carrying Capacity & Temperature Rising Table
(Width × Thickness) | Temperature rising(K) under Ambient Temperature 25℃ (Ampere) | |||||
mm × mm | Cu =25% | Cu =30% | ||||
50K | 65K | 75K | 50K | 65K | 75K | |
15.00×4.00 | 196 | 210 | 225 | 200 | 213 | 229 |
20.00×4.00 | 254 | 273 | 293 | 259 | 277 | 298 |
25.00×4.00 | 314 | 339 | 363 | 321 | 345 | 370 |
30.00×4.00 | 336 | 362 | 387 | 347 | 372 | 399 |
30.00×5.00 | 438 | 453 | 489 | 450 | 466 | 503 |
30.00×6.00 | 499 | 539 | 579 | 514 | 554 | 595 |
30.00×8.00 | 596 | 644 | 697 | 613 | 662 | 717 |
30.00×10.00 | 658 | 712 | 745 | 676 | 733 | 767 |
40.00×4.00 | 465 | 500 | 532 | 479 | 513 | 547 |
40.00×5.00 | 554 | 605 | 652 | 570 | 622 | 670 |
40.00×6.00 | 630 | 679 | 728 | 649 | 698 | 750 |
40.00×8.00 | 746 | 806 | 873 | 767 | 829 | 897 |
40.00×10.00 | 814 | 896 | 977 | 837 | 921 | 1005 |
50.00×5.00 | 684 | 736 | 788 | 703 | 758 | 810 |
50.00×6.00 | 777 | 836 | 898 | 799 | 861 | 923 |
50.00×8.00 | 918 | 990 | 1072 | 944 | 1019 | 1103 |
50.00×10.00 | 998 | 1061 | 1139 | 1026 | 1092 | 1172 |
60.00×5.00 | 781 | 858 | 918 | 804 | 882 | 945 |
60.00×6.00 | 886 | 953 | 1025 | 911 | 980 | 1053 |
60.00×8.00 | 1041 | 1124 | 1216 | 1070 | 1156 | 1252 |
60.00×10.00 | 1125 | 1218 | 1318 | 1157 | 1253 | 1355 |
80.00×6.00 | 1113 | 1198 | 1287 | 1145 | 1232 | 1323 |
80.00×8.00 | 1302 | 1407 | 1523 | 1340 | 1448 | 1566 |
80.00×10.00 | 1402 | 1507 | 1629 | 1442 | 1550 | 1676 |
100.00×6.00 | 1320 | 1422 | 1527 | 1358 | 1462 | 1571 |
100.00×8.00 | 1548 | 1672 | 1811 | 1593 | 1719 | 1862 |
100.00×10.00 | 1668 | 1793 | 1938 | 1716 | 1844 | 1993 |
120.00×8.00 | 1791 | 1935 | 2095 | 1842 | 1990 | 2154 |
120.00×10.00 | 1946 | 2094 | 2261 | 2002 | 2153 | 2326 |
The reference of standard: ASTM-B1005